Hazardous Area Study
NR 10 defines the obligation to carry out the Hazardous Area Study , where there is the possibility of the formation of a potentially explosive atmosphere, due to the storage or handling of flammable or combustible substances, as defined in items 10.2.4.f, 10.8.8.4, 10.9.2, which determine that the installation and equipment are suitable for the Classification of Areas.
Flammable gases and vapors, as well as combustible dust, can generate explosive atmospheres. Industries that may have explosive atmospheres include:
• Oil refineries, platforms and processing plants with terrestrial (onshore) or maritime (offshore) locations;
• Oil and gas loading ships, drilling rigs and FPSOs (Floating Production Storage Offloading);
• Petrochemical and chemical processing plants;
• Paint, paper and fabric industries;
• Surgical centers in hospitals;
• Refueling stations and aircraft hangars
• Industries of metallic surface coatings;
• Underground coal mines;
• Sewage treatment plants;
• Gas pipelines and gas distribution centers;
• Grain handling, storage and processing industries (food and silage industry);
• Furniture industry;
• Sugar and ethanol refineries;
• Work with light alloy metals where metal dust and particulate material may be present.
• Service stations for refueling vehicles;
• Pharmaceutical and Food Laboratories
Standards for the Hazardous Area Study
The main ABNT Standards for the preparation of the Area Classification Study are NBR IEC 60079-10-1 - Classification of areas - Explosive gas atmospheres and NBR IEC 60079-20-1 - Classification of areas - Combustible Dusts
Factors considered in Classified Areas: ZONE - Group - Temperature Class
ZONE definition for explosive gas atmospheres:
-
ZONE 0 - Area where the occurrence of a flammable / explosive mixture is continuous
-
ZONE 1 - Area where the occurrence of a flammable / explosive mixture is likely to occur under normal operating conditions of the process equipment
-
ZONE 2 - Area where the occurrence of a flammable / explosive mixture is unlikely to happen, and if it does, it is for short periods, and is associated with the abnormal operation of the process equipment.
ZONE definition for combustible dust explosive atmospheres
-
Zone 20 - A place where an explosive atmosphere, in the form of a cloud of combustible dust, is present in the air continuously, for long periods of time or frequently
-
Zone 21 - A place where an explosive atmosphere, in the form of a cloud of combustible dust in the air, is expected to eventually occur under normal operating conditions
-
Zone 22 - A place where an explosive atmosphere, in the form of a combustible dust cloud in the air, is not expected to occur in normal operation, but if it does, it will only remain for a brief period of time.

Paulo Sampaio and Roberval Bulgarelli
Field inspections of instrumentation, automation, telecommunications and electrical equipment and installations in classified areas containing flammable gases and combustible dust in the chemical industry in Rio de Janeiro.
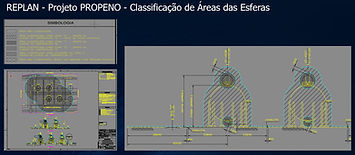
Graneleiro Bus Terminal Area Classification Plant and Memorial.

Safety management of “Ex” equipment and installations
Field inspections of instrumentation, automation, telecommunications and electrical equipment and installations in classified areas containing flammable gases and combustible dust in the chemical industry in Rio de Janeiro.
Application of the “Ex” checklists indicated in the adopted Brazilian Technical Standard ABNT NBR IEC 60079-17 - Inspection and maintenance of equipment and installations in explosive atmospheres, according to the degree of inspection adopted and the types of “Ex” protection of the inspected equipment.
Use of electronic inspection system, based on reports generated on tablets.
Presentation of the necessary actions necessary to correct the “Ex” deviations found, as well as actions for the implementation of an adequate “Ex” asset management system, including registration of the “Ex” equipment inventory, “Ex” periodic inspection system and “Ex” personal skills training and certification.
Example of Equipment Inspection Report for classified areas



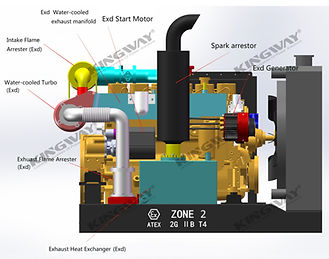
Ex Motor
Gestão de segurança de equipamentos Não Elétricos “Ex”
As Normas as normas ABNT NBR ISO 80079-36 - Equipamentos não elétricos para atmosferas explosivas - Métodos - requisitos básicos e ABNT NBR ISO 80079-37 - Equipamentos não elétricos para atmosferas explosivas - Tipos de Proteção, definem a forma de avaliação dos equipamentos mecânicos instalados em Áreas Classificadas.
Possíveis Fontes de Ignição
Conforme a Norma ABNT NBR ISO 80079-36 existem treze possíveis fontes de ignição que podem causar a explosão de atmosferas explosivas de gases inflamáveis ou poeiras combustíveis:
Superfícies quentes
Chamas ou gases aquecidos, incluindo partículas quentes
Faíscas geradas mecanicamente
Dispositivos elétricos (centelhas geradas eletricamente)
Correntes parasitas ou proteção catódica de corrosão
Eletricidade estática
Descargas atmosféricas
Radiofrequência ou ondas eletromagnéticas
Radiação óptica
Radiação ionizante
Ultrassom
Compressão adiabática e ondas de choque
Reações exotérmicas, incluindo a autoignição de poeiras combustíveis
Equipamentos Mecânicos que podem provocar a ignição de Atmosferas Explosivas
Compressores: Equipamentos utilizados para comprimir gases ou ar.
Ventiladores: Responsáveis pela movimentação do ar em sistemas industriais.
Bombas: Utilizadas para transferir líquidos ou fluidos.
Agitadores ou Misturadores para Tanques: Equipamentos para homogeneização de líquidos.
Freios: Componentes de segurança em máquinas rotativas.
Acoplamentos para Equipamentos Rotativos: Conectam e transmitem torque entre eixos.
Medidores Rotativos: Utilizados para medição de vazão de fluidos.
Motores Hidráulicos e Pneumáticos: Motores que funcionam com fluidos.
Skids para Medição de Gás: Conjuntos de equipamentos compactos para medição de gás.
Caixas com Engrenagens de Velocidade: Caixas de engrenagens para transmissão de Movimento.
Válvulas: Dispositivos para controle de fluxo de fluidos.
Transmissores de Pressão: Equipamentos para medição e transmissão de pressão.
Sensores de Temperatura: Detectam variações de temperatura.
Atuadores: Componentes que transformam energia em movimento.
Filtros: Utilizados para purificação de fluidos.
Rolamentos: Componentes para suporte e movimentação de eixos.
Engrenagens: Transmitem torque entre eixos.
Correias Transportadoras: para transporte de granulados.
Sistemas de Coleta de Poeira: Dispositivos para extração de poeiras suspensas
Tipos de Certificados para Equipamentos Mecânicos “Ex”
Os equipamentos Mecânicos instalados em Áreas Classificadas devem ser Certificados e receber a marcação “Ex”, com especificação adequada ao tipo de Zona, Classe de Temperatura, Grupo do Produto que foi ensaiado e temperatura máxima (interna ou de superfície).
Ex “h” - Equipamento mecânico “Ex”
Ex “b” - Controle das fontes de ignição
Ex “c” - Segurança construtiva
Ex “k” - Imersão em líquido